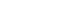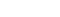| 제목 |
determining the peak cough flow values to predict dysphagia in stroke patients |
| 소속 |
Bucheon, St. Mary’s Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Department of Rehabilitation Medicine1 |
| 저자 |
Hyunhwa Lee MD.1*, Yeonjae Han MD.1, Geun-Young Park MD, Ph.D. 1, Sun Im MD, Ph.D. 1† |
Objective
Cough failure in patients may be a life-threatening condition leading to aspiration pneumonia. Ineffective cough production is associated with a higher prevalence of respiratory complications in stroke. In our study, to determine the diagnostic parameters and appropriate cut-off values of the cough strength, we assessed, the maximal inspiratory and expiratory pressures and peak cough flow to determine which parameter could accurately screen presence dysphagia in stroke patients.
Method
Retrospective analysis of a prospectively maintained database was done. in a single university affiliated hospital. Patients with first-ever diagnosed dysphagia attributable to cerebrovascular disease, prospectively performed spirometry measurements for the voluntary peak cough flow and respiratory pressure meters were recruited. These values were compared to patients with no evidence of dysphagia after stroke. Primary outcome measures were peak cough flow (L/min) during voluntary coughing and maximal pressure meter (cmH22O)).
Results
Total eligible patients (N=237) with 163 patients who were diagnosed with dysphagia related to stroke were recruited. A final 163 patients had full medical records with 6-month follow-up. Receiver operating curve analysis showed that peak cough flow cut-off values set at 151 L/min were significantly associated with presence of dysphagia with sensitivity levels of 0.72 (0.66-0.79) and specificity levels of 0.78 (0.69-0.88) [area under the curve (AUC) 95% confidence interval (CI)=0.81 (0.76-0.87)] [fig.1]. In contrast, the cut-off values set at 20 and 38 for the MIP and MEP showed lower sensitivity levels (0.49, 0.58) with lower AUC values of 0.65(0.58-0.72) and 0.70(0.64- 0.77).Peak cough flow, as an independent predictor of dysphagia in stroke patients, could significantly predict the presence of dysphagia with an adjusted odds ratio of 4.12 (2.20-8.69, p<0.001) in a multivariate logistic regression analysis [fig.2].
Conclusions
Among the various respiratory parameters, the peak cough flow cut-off values of the voluntary cough flow set at 151 L/min can significantly indicate the presence of dysphagia. Results advocate the objective measurement of peak cough flow from voluntary coughing to be used as part of the formal assessment those with post-stroke dysphagia. Our results indicate that among the various respiratory parameters, objective strength measurement of the peak cough flow could help screen those with dysphagia.
|
|
Peak cough flow cut-off values set at 151 L/min were associated with presence of dysphagia [area under the curve (AUC) 95% confidence interval (CI) = 0.81 (0.76–0.87)]
Peak cough flow, as an independent predictor of dysphagia in stroke patients, could significantly predict the presence of dysphagia in a multivariate logistic regression analysis
|